How To Find Number Of Unknowns In Matrix
Solving Systems of Linear Equations Using Matrices
Homogeneous and non-homogeneous systems of linear equations
A system of equations AX = B is chosen a homogeneous organisation if B = O. If B ≠ O, it is chosen a not-homogeneous system of equations.
east.g., 2x + 5y = 0
3x – 2y = 0
is a homogeneous arrangement of linear equations whereas the system of equations given by
e.g., 2x + 3y = 5
10 + y = two
is a non-homogeneous organisation of linear equations.
Solution of Non-homogeneous system of linear equations
- Matrix method: If AX = B, and so X = A-oneB gives a unique solution, provided A is not-singular.
But if A is a atypical matrix i.e., if |A| = 0, then the system of equation AX = B may be consistent with infinitely many solutions or it may exist inconsistent. - Rank method for solution of Not-Homogeneous system AX = B
- Write down A, B
- Write the augmented matrix [A : B]
- Reduce the augmented matrix to Echelon course by using elementary row operations.
- Find the number of non-null rows in A and [A : B] to find the ranks of A and [A : B] respectively.
- If ρ(A) ≠ ρ(A : B) and then the system is inconsistent.
- ρ(A) = ρ(A : B) = the number of unknowns, and so the system has a unique solution.
- ρ(A) = ρ(A : B) < number of unknowns, and so the organisation has an infinite number of solutions.
Solutions of a homogeneous system of linear equations
Let AX = O be a homogeneous system of 3 linear equations in 3 unknowns.
- Write the given system of equations in the course AX = O and write A.
- Find |A|.
- If |A| ≠ 0, and so the organization is consistent and x = y = z = 0 is the unique solution.
- If |A| = 0, then the systems of equations has infinitely many solutions. In order to detect that put z = k (whatsoever existent number) and solve whatever two equations for x and y so obtained with z = k give a solution of the given system of equations.
Consistency of a organisation of linear equation AX = B, where A is a square matrix
In system of linear equations AX = B, A = (aij)n ×north is said to exist
- Consequent (with unique solution) if |A| ≠ 0.
i.e., if A is non-singular matrix. - Inconsistent (It has no solution) if |A| = 0 and (adj A)B is a not-naught matrix.
- Consequent (with infinitely yard any solutions) if |A| = 0 and (adj A)B is a null matrix.
Rank of matrix
Definition:
Let A be a thou×n matrix. If we retain whatever r rows and r columns of A we shall accept a square sub-matrix of guild r. The determinant of the square sub-matrix of society r is called a minor of A gild r. Consider any matrix A which is of the order of 3×iv say,
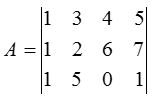 .
.
Information technology is 3×4 matrix so we tin can have minors of order 3, 2 or i. Taking whatsoever three rows and three columns minor of order three. Hence pocket-sized of lodge \(iii=\left| \begin{matrix} 1 & 3 & four \\ 1 & 2 & 6 \\ 1 & 5 & 0 \end{matrix} \correct| =0\)
Making ii zeros and expanding above minor is cypher. Similarly we tin consider any other minor of club 3 and it tin be shown to exist zero. Minor of order 2 is obtained by taking whatever ii rows and whatever two columns.
Minor of order \(2=\brainstorm{vmatrix} 1 & 3 \\ one & 2 \end{vmatrix}=2-3=-1\neq 0\).
Small-scale of order 1 is every element of the matrix.
Rank of a matrix: The rank of a given matrix A is said to exist r if
- Every pocket-size of A of order r+i is zero.
- There is at least one pocket-size of A of order r which does not vanish. Here we can also say that the rank of a matrix A is said to exist r ,if
- Every square submatrix of order r+1 is singular.
- There is at least ane square submatrix of society r which is non-singular.
The rank r of matrix A is written as ρ(A) = r.
Echelon form of a matrix
A matrix A is said to exist in Echelon form if either A is the null matrix or A satisfies the following weather:
- Every non- nix row in A precedes every zilch row.
- The number of zeros before the kickoff not-goose egg element in a row is less than the number of such zeros in the adjacent row.
If tin can be easily proved that the rank of a matrix in Echelon course is equal to the number of non-aught row of the matrix.
Rank of a matrix in Echelon form: The rank of a matrix in Echelon form is equal to the number of non-zero rows in that matrix.
Solving Systems of Linear Equations Using Matrices Problems with Solutions
one.
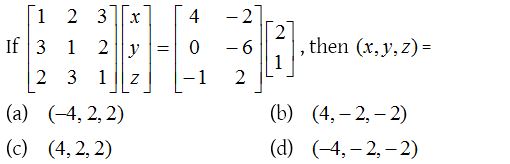
Solution:
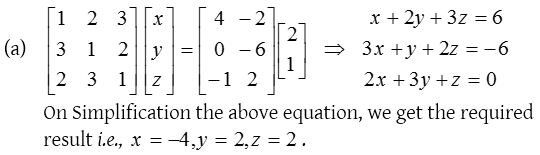
ii.
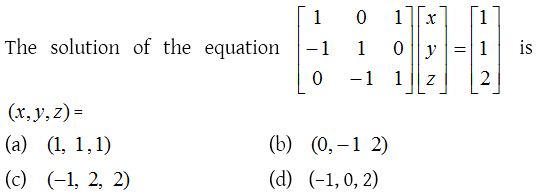
Solution:

three.
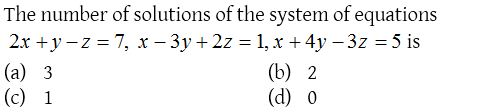
Solution:
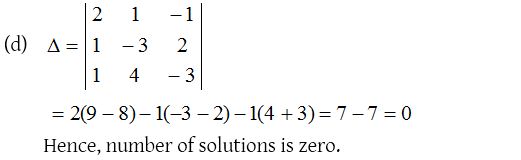
4.

Solution:

five.
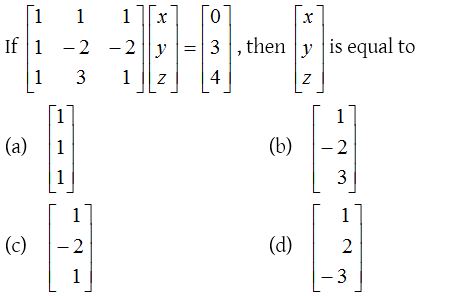
Solution:
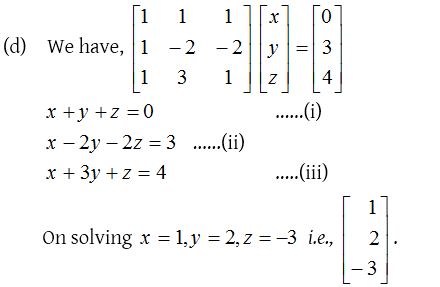
Source: https://www.aplustopper.com/solving-systems-linear-equations-using-matrices/

0 Response to "How To Find Number Of Unknowns In Matrix"
Post a Comment